
中国水稻科学 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 320-326.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6136 320
收稿日期:2016-10-20
修回日期:2016-11-30
出版日期:2017-05-10
发布日期:2017-05-10
通讯作者:
周而勋
Minghai ZHU, Lei PI, Canwei SHU, Erxun ZHOU*( )
)
Received:2016-10-20
Revised:2016-11-30
Online:2017-05-10
Published:2017-05-10
Contact:
Erxun ZHOU
摘要:
【目的】为了明确南繁区稻瘟病菌(Magnaporthe oryzae)的遗传分化情况,【方法】采用AFLP分子标记技术对南繁核心区(三亚、乐东和保亭)和非核心区(琼中、屯昌和定安)共60个稻瘟病菌菌株的遗传多样性和群体遗传结构进行了比较分析。【结果】聚类分析表明,几乎所有菌株都聚在同一个谱系里,并且该谱系没有明显的亚群;群体遗传结构分析表明,核心区群体的多态性位点百分率、Shannon信息指数和基因流分别为 87.89%、0.2738和4.2897,高于非核心区群体的 81.37%、0.2703和3.5892;然而,核心区群体的Nei基因多样性指数和基因分化系数分别为 0.1657和0.1044,低于非核心区群体的 0.1662和0.1223。【结论】这些结果表明核心区和非核心区菌株都存在丰富的遗传多样性,不同群体间均存在较多的基因交流,但遗传变异均主要来自群体内;相比之下,核心区菌株的遗传多样性和遗传分化程度较高。
中图分类号:
朱名海, 皮磊, 舒灿伟, 周而勋. 南繁区稻瘟病菌遗传多样性和群体遗传结构的AFLP分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 320-326.
Minghai ZHU, Lei PI, Canwei SHU, Erxun ZHOU. AFLP Analyses of Genetic Diversity and Population Genetic Structure of Magnaporthe oryzae from South China Crop Breeding Area[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(3): 320-326.
| 区域 Region | 采集地点 Sampling location | 菌株编号 Isolate No. | 采集时间 Sampling date | 水稻类型 Rice type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南繁核心区Core region | |||||||
| 三亚Sanya | 育才镇国营立才农场 | P1, P2, P3 | 2015-05-20 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 吉阳镇大茅村 | P4, P5, P6 | 2014-10-24 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 吉阳镇罗蓬村 | P7, P8 | 2014-10-24 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 育才镇雅亮村 | P9, P10 | 2014-10-29 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 乐东Ledong | 抱由镇城郊 | P11, P12, P13 | 2014-10-22 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 利国镇新丰田洋 | P14, P15, P16 | 2014-10-20 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 千家镇农技实验站 | P17, P18, P19, P20 | 2014-10-20 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 保亭Baoting | 加茂镇灶长村 | P21, P22, P23, P24, P25, P26, P27, P28, P29, P30 | 2015-05-15 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 南繁非核心区Non-core region | |||||||
| 琼中Qiongzhong | 长征镇长征农场 | P31, P32, P33, P34, P35, P36, P37, P38, P39, P40 | 2015-05-18 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 屯昌Tunchang | 屯城镇良史村 | P41, P42, P43, P44, P45, P46, P47, P48, P49, P50 | 2015-05-18 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 定安Ding’an | 新竹镇新序村 | P51, P52, P53, P54, P55, P56, P57, P58, P59, P60 | 2015-05-17 | 籼稻 indica | |||
表1 南繁核心区和非核心区稻瘟病菌的详细情况
Table 1 The details of Magnaporthe oryzae in the core and non-core regions of South China Crop Breeding Area.
| 区域 Region | 采集地点 Sampling location | 菌株编号 Isolate No. | 采集时间 Sampling date | 水稻类型 Rice type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南繁核心区Core region | |||||||
| 三亚Sanya | 育才镇国营立才农场 | P1, P2, P3 | 2015-05-20 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 吉阳镇大茅村 | P4, P5, P6 | 2014-10-24 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 吉阳镇罗蓬村 | P7, P8 | 2014-10-24 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 育才镇雅亮村 | P9, P10 | 2014-10-29 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 乐东Ledong | 抱由镇城郊 | P11, P12, P13 | 2014-10-22 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 利国镇新丰田洋 | P14, P15, P16 | 2014-10-20 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 千家镇农技实验站 | P17, P18, P19, P20 | 2014-10-20 | 籼稻 indica | ||||
| 保亭Baoting | 加茂镇灶长村 | P21, P22, P23, P24, P25, P26, P27, P28, P29, P30 | 2015-05-15 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 南繁非核心区Non-core region | |||||||
| 琼中Qiongzhong | 长征镇长征农场 | P31, P32, P33, P34, P35, P36, P37, P38, P39, P40 | 2015-05-18 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 屯昌Tunchang | 屯城镇良史村 | P41, P42, P43, P44, P45, P46, P47, P48, P49, P50 | 2015-05-18 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 定安Ding’an | 新竹镇新序村 | P51, P52, P53, P54, P55, P56, P57, P58, P59, P60 | 2015-05-17 | 籼稻 indica | |||
| 序号 Code | 接头名称 Adapter name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5′→3′) | 引物用途 Purpose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ea | EcoRⅠ接头 EcoRⅠadapter | CTCGTAGACTGCGTACC CATCTGACGCATGGTTAA | 连接 Connection | |
| Em | MseⅠ接头 MseⅠadapter | GACGATGAGTCCTGAG TACTCAGGACTCAT | 连接 Connection | |
| E0 | EcoRⅠ+0 | GACTGCGTACCAATTC | 预扩增 Pre-amplification | |
| E1 | EcoRⅠ+AAC | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAAC | 选择性扩增Selective amplification analysis | |
| E2 | EcoRⅠ+ACA | GACTGCGTACCAATTCACA | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E3 | EcoRⅠ+ACG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCACG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E4 | EcoRⅠ+AGG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAGG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E5 | EcoRⅠ+AAG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAAG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E6 | EcoRⅠ+ACT | GACTGCGTACCAATTCACT | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E7 | EcoRⅠ+ACC | GACTGCGTACCAATTCACC | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E8 | EcoRⅠ+AGC | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAGC | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M0 | MseⅠ+0 | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAA | 预扩增预扩增 Pre-amplification | |
| M1 | MseⅠ+CAA | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAA | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M2 | MseⅠ+CAT | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAT | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M3 | MseⅠ+CAC | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAC | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M4 | MseⅠ+CAG | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M5 | MseⅠ+ CTA | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACTA | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M6 | MseⅠ+CTT | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACTT | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M7 | MseⅠ+CTC | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACTC | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M8 | MseⅠ+CTG | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACTG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
表2 AFLP所用接头和引物
Table 2 Adapters and primers for AFLP.
| 序号 Code | 接头名称 Adapter name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5′→3′) | 引物用途 Purpose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ea | EcoRⅠ接头 EcoRⅠadapter | CTCGTAGACTGCGTACC CATCTGACGCATGGTTAA | 连接 Connection | |
| Em | MseⅠ接头 MseⅠadapter | GACGATGAGTCCTGAG TACTCAGGACTCAT | 连接 Connection | |
| E0 | EcoRⅠ+0 | GACTGCGTACCAATTC | 预扩增 Pre-amplification | |
| E1 | EcoRⅠ+AAC | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAAC | 选择性扩增Selective amplification analysis | |
| E2 | EcoRⅠ+ACA | GACTGCGTACCAATTCACA | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E3 | EcoRⅠ+ACG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCACG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E4 | EcoRⅠ+AGG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAGG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E5 | EcoRⅠ+AAG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAAG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E6 | EcoRⅠ+ACT | GACTGCGTACCAATTCACT | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E7 | EcoRⅠ+ACC | GACTGCGTACCAATTCACC | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| E8 | EcoRⅠ+AGC | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAGC | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M0 | MseⅠ+0 | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAA | 预扩增预扩增 Pre-amplification | |
| M1 | MseⅠ+CAA | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAA | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M2 | MseⅠ+CAT | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAT | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M3 | MseⅠ+CAC | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAC | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M4 | MseⅠ+CAG | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACAG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M5 | MseⅠ+ CTA | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACTA | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M6 | MseⅠ+CTT | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACTT | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M7 | MseⅠ+CTC | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACTC | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| M8 | MseⅠ+CTG | GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACTG | 选择性扩增 Selective amplification analysis | |
| 引物组合 Primer combination | 扩增条带数 Amplification band number | 多态性条带数 Polymorphic band number | 多态性条带百分率 Percentage of polymorphic band/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| E2/M1 | 41 | 40 | 97.56 |
| E2/M2 | 51 | 51 | 100.00 |
| E3/M4 | 44 | 44 | 100.00 |
| E3/M5 | 51 | 51 | 100.00 |
| E4/M5 | 38 | 38 | 100.00 |
| E4/M6 | 47 | 47 | 100.00 |
| E4/M8 | 35 | 35 | 100.00 |
| E5/M1 | 49 | 49 | 100.00 |
| E5/M4 | 57 | 56 | 98.25 |
| 总计Total | 413 | 411 | 99.52 |
表3 南繁核心区和非核心区稻瘟病菌AFLP引物组合的扩增结果统计
Table 3 The amplification results of AFLP primer combinations for Magnaporthe oryzae in the core and non-core regions of South China Crop Breeding Area.
| 引物组合 Primer combination | 扩增条带数 Amplification band number | 多态性条带数 Polymorphic band number | 多态性条带百分率 Percentage of polymorphic band/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| E2/M1 | 41 | 40 | 97.56 |
| E2/M2 | 51 | 51 | 100.00 |
| E3/M4 | 44 | 44 | 100.00 |
| E3/M5 | 51 | 51 | 100.00 |
| E4/M5 | 38 | 38 | 100.00 |
| E4/M6 | 47 | 47 | 100.00 |
| E4/M8 | 35 | 35 | 100.00 |
| E5/M1 | 49 | 49 | 100.00 |
| E5/M4 | 57 | 56 | 98.25 |
| 总计Total | 413 | 411 | 99.52 |
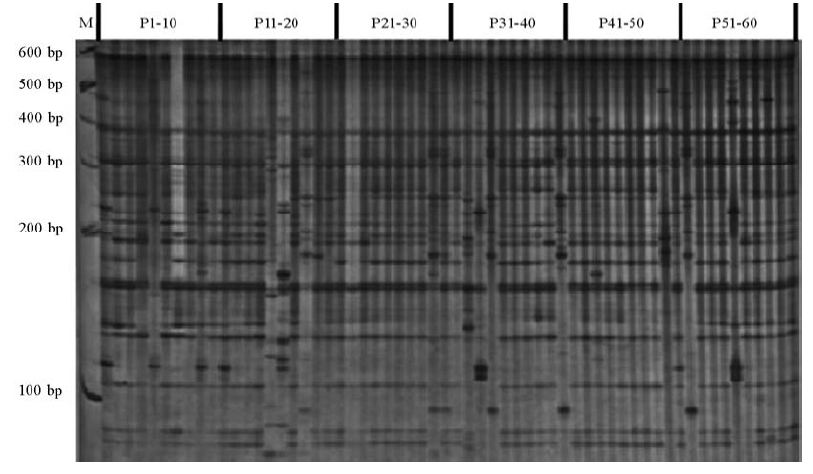
图1 引物组合E5/M4扩增的稻瘟病菌AFLP分析结果 M为GeneRule 100 bp DNA梯度标记;P1-P60为菌株编号。
Fig. 1. AFLP results for Magnaporthe oryzae with the primer combination E5/M4.M, GeneRule 100 bp DNA ladder marker; P1-P60 are the isolate numbers.
| 群体 Population | 菌株数 No. of isolates | 总位点数 No. of total loci | 多态性位点数 No. of polymorphic loci | 多态性位点百分率Percentage of polymorphic loci/% | Shannon信息指数 Shannon information index | Nei基因多样性指数 Gene diversity index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三亚Sanya | 10 | 413 | 157 | 38.01 | 0.1757 | 0.1149 |
| 乐东Ledong | 10 | 413 | 332 | 80.39 | 0.3156 | 0.1982 |
| 保亭Baoting | 10 | 413 | 206 | 49.88 | 0.2074 | 0.1322 |
| 琼中Qiongzhong | 10 | 413 | 282 | 68.28 | 0.3132 | 0.2025 |
| 屯昌Tunchang | 10 | 413 | 128 | 30.99 | 0.1283 | 0.0815 |
| 定安Ding’an | 10 | 413 | 245 | 59.32 | 0.2408 | 0.1535 |
| 核心区Core region | 30 | 413 | 363 | 87.89 | 0.2738 | 0.1657 |
| 非核心区Non-core region | 30 | 413 | 336 | 81.37 | 0.2703 | 0.1662 |
| 总物种Total | 60 | 413 | 411 | 99.52 | 0.2821 | 0.1701 |
表4 南繁核心区和非核心区稻瘟病菌不同群体的遗传多样性分析
Table 4 Genetic diversity analyses of different Magnaporthe oryzae populations in the core and non-core regions of South China Crop Breeding Area.
| 群体 Population | 菌株数 No. of isolates | 总位点数 No. of total loci | 多态性位点数 No. of polymorphic loci | 多态性位点百分率Percentage of polymorphic loci/% | Shannon信息指数 Shannon information index | Nei基因多样性指数 Gene diversity index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三亚Sanya | 10 | 413 | 157 | 38.01 | 0.1757 | 0.1149 |
| 乐东Ledong | 10 | 413 | 332 | 80.39 | 0.3156 | 0.1982 |
| 保亭Baoting | 10 | 413 | 206 | 49.88 | 0.2074 | 0.1322 |
| 琼中Qiongzhong | 10 | 413 | 282 | 68.28 | 0.3132 | 0.2025 |
| 屯昌Tunchang | 10 | 413 | 128 | 30.99 | 0.1283 | 0.0815 |
| 定安Ding’an | 10 | 413 | 245 | 59.32 | 0.2408 | 0.1535 |
| 核心区Core region | 30 | 413 | 363 | 87.89 | 0.2738 | 0.1657 |
| 非核心区Non-core region | 30 | 413 | 336 | 81.37 | 0.2703 | 0.1662 |
| 总物种Total | 60 | 413 | 411 | 99.52 | 0.2821 | 0.1701 |
| 群体Population | 群体总基因多样性 Total genetic diversity in populations | 群体内基因多样性 Genetic diversity within population | 基因分化度Genetic differentiation coefficient | 基因流 Gene flow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 核心区Core region | 0.1657 | 0.1484 | 0.1044 | 4.2897 |
| 非核心区Non-core region | 0.1662 | 0.1459 | 0.1223 | 3.5892 |
| 总物种Total | 0.1701 | 0.1472 | 0.1348 | 3.2092 |
表5 南繁核心区和非核心区稻瘟病菌群体的遗传分化和基因流
Table 5 Genetic differentiation and gene flow of different populations of Magnaporthe oryzae from the core and non-core regions of South China Crop Breeding Area.
| 群体Population | 群体总基因多样性 Total genetic diversity in populations | 群体内基因多样性 Genetic diversity within population | 基因分化度Genetic differentiation coefficient | 基因流 Gene flow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 核心区Core region | 0.1657 | 0.1484 | 0.1044 | 4.2897 |
| 非核心区Non-core region | 0.1662 | 0.1459 | 0.1223 | 3.5892 |
| 总物种Total | 0.1701 | 0.1472 | 0.1348 | 3.2092 |
| 群体 Population | 三亚 Sanya | 乐东 Ledong | 保亭 Baoting | 琼中 Qiongzhong | 屯昌 Tunchang | 定安 Ding’an |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三亚Sanya | 0.9662 | 0.9700 | 0.9518 | 0.9675 | 0.9673 | |
| 乐东Ledong | 0.0344 | 0.9744 | 0.9779 | 0.9612 | 0.9796 | |
| 保亭Baoting | 0.0305 | 0.0260 | 0.9702 | 0.9719 | 0.9737 | |
| 琼中Qiongzhong | 0.0494 | 0.0224 | 0.0303 | 0.9502 | 0.9759 | |
| 屯昌Tunchang | 0.0331 | 0.0396 | 0.0285 | 0.0511 | 0.9708 | |
| 定安Ding’an | 0.0333 | 0.0206 | 0.0267 | 0.0244 | 0.0296 |
表6 南繁核心区和非核心区稻瘟病菌群体的遗传一致性和遗传距离
Table 6 Genetic identity and genetic distance of different Magnaporthe oryzae populations from the core and non-core regions of South China Crop Breeding Area.
| 群体 Population | 三亚 Sanya | 乐东 Ledong | 保亭 Baoting | 琼中 Qiongzhong | 屯昌 Tunchang | 定安 Ding’an |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三亚Sanya | 0.9662 | 0.9700 | 0.9518 | 0.9675 | 0.9673 | |
| 乐东Ledong | 0.0344 | 0.9744 | 0.9779 | 0.9612 | 0.9796 | |
| 保亭Baoting | 0.0305 | 0.0260 | 0.9702 | 0.9719 | 0.9737 | |
| 琼中Qiongzhong | 0.0494 | 0.0224 | 0.0303 | 0.9502 | 0.9759 | |
| 屯昌Tunchang | 0.0331 | 0.0396 | 0.0285 | 0.0511 | 0.9708 | |
| 定安Ding’an | 0.0333 | 0.0206 | 0.0267 | 0.0244 | 0.0296 |

图3 基于Nei遗传一致性的南繁核心区和非核心区稻瘟病菌群体聚类图
Fig. 3. Clustering analyses of Magnaporthe oryzae from the core and non-core regions of South China Crop Breeding Area based on Nei's genetic consistency.
| [1] | 陈冠铭, 李劲松, 曹兵. 发挥南繁资源优势促进种业科技创新. 安徽农学通报, 2012, 18(1): 27-29. |
| Chen G M, Li J S, Cao B.Make the most of resources’ advantages of Hainan national multiplication, promoting Sci-Tech innovations of seed industry.Anhui Agric Sci Bull, 2012, 18(1): 27-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 陈冠铭, 李劲松, 林亚琼. 国家南繁功能价值与发展机遇研究分析. 种子, 2012, 31(3): 69-71. |
| Chen G M, Li J S, Lin Y Q.Research and analysis on the functional value and development opportunities of Hainan national breeding and multiplication.Seed, 2012, 31(3): 69-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 赵文生. 水稻稻瘟病发病规律与防治措施. 科技创新与应用, 2012(1): 187. |
| Zhao W S. The occurrence and control of rice sheath blight. Technol Innov Applic, 2012(1): 187. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 李小闯. 稻瘟病的危害与综合防治. 农技服务, 2010, 27(12): 1585-1586. |
| Li X C.The damage and integrated control of rice blast.Agric Technol Serv, 2010, 27(12): 1585-1586. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Zhang H, Zheng X, Zhang Z.The Magnaporthe grisea species complex and plant pathogenesis.Mol Plant Pathol, 2015, 17(6): 796-804. |
| [6] | Miah G, Rafii M Y, Ismail M R, Puteh A B, Rahim H A, Asfaliza R, Latif M A.Blast resistance in rice: A review of conventional breeding to molecular approaches.Mol Biol Rep, 2013, 40(3): 2369-2388. |
| [7] | 沈瑛, 袁筱萍, 王艳丽. 分子探针在稻瘟病流行病学中的应用研究. 西南农业大学学报, 1998, 20(5): 401-408. |
| Shen Y, Yuan X P, Wang Y L.Molecular probes for epidemiological studies of the rice blast fungus.J Southwest Agric Univ, 1998, 20(5): 401-408. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Séré Y, Onasanya A, Afolabi A, Mignouna H D, Akator K.Genetic diversity of the blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea (Hebert) Barr, in Burkina Faso.Afric J Biotechnol, 2007, 6(22): 2568-2577. |
| [9] | Choi J, Kim H, Lee Y H.Comparative analysis of the Korean population of Magnaporthe oryzae by multilocus microsatellite typing.Plant Pathol J, 2013, 29(4): 435-439. |
| [10] | Taheri P, Irannejad A.Genetic structure of various Magnaporthe oryzae populations in Iran and Uruguay.Aus Plant Pathol, 2014, 43(3): 287-297. |
| [11] | Masoud N G, Gholamreza S J, Mohammad J M.Characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Magnaporthe spp. strains on various hosts in Iran. Ir J Biotechnol, 2014, 12(3): 71-81. |
| [12] | Takan J P, Chipili J, Muthumeenakshi S, Talbot N J, Manyasa E O, Bandyopadhyay R, Sere Y, Nutsugah S K, Talhinhas P, Hossain M, Brown A E.Magnaporthe oryzae populations adapted to finger millet and rice exhibit distinctive patterns of genetic diversity, sexuality and host interaction.Mol Biotechnol, 2012, 50(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | Chen Q H, Wang Y C, Zheng X B.Genetic diversity of Magnaporthe grisea in China as revealed by DNA fingerprint haplotypes and pathotypes. J Phytopathol, 2006, 154(6): 361-369. |
| [14] | Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Lee T V D, Hornes M, Fritjers A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M. AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting.Nucleic Acids Res, 1995, 23(21): 4407-4414. |
| [15] | 李珊, 赵桂仿. AFLP分子标记及其应用. 西北植物学报, 2003, 23(5): 830-836. |
| Li S, Zhao G F.AFLP molecular marker and its application.Acta Bot Boreali-Occ Sin, 2003, 23(5): 830-836. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Sanguinetti C J, Dias N E, Simpson A J.Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels.Biotechniques, 1994, 17(5): 914-921. |
| [17] | 刘振华, 李晓菲, 王园媛, 陈涛, 王云月. 云南省稻瘟病菌群体遗传结构研究. 云南农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 28(1): 9-15. |
| Liu Z H, Li X F, Wang Y Y, Chen T, Wang Y Y.Investigation on population genetic structure of Magnaporthe grisea in Yunnan.J Yunnan Agric Univ: Nat Sci, 2013, 28(1): 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 张亚玲, 王宝玉, 台莲梅, 豫虎, 郑雯, 邓本良, 靳学慧. 黑龙江省和吉林省稻瘟病菌种群多样性研究. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2014, 26(1): 1-4, 31. |
| Zhang Y L, Wang B Y, Tai L M, Yu H, Zheng W, Deng B L, Jin X H.Study of population structure of Magnaporthe oryzae from rice in Heilongjiang and Jilin.J Heilongjiang Bayi Agri Univ, 2014, 26(1): 1-4, 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 王玲, 左示敏, 张亚芳, 陈宗祥, 潘学彪, 黄世文. 四川省稻瘟病菌群体遗传结构分析. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 327-334. |
| Wang L, Zuo S M, Zhang Y F, Chen Z X, Pan X B, Huang S W.Genetic structure of rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae in Sichuan Province.Chin J Rice Sci, 2015, 29(3): 327-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 吴玥, 梁铖玮, 赵辰妃, 孙健, 马殿荣. 直播稻田杂草稻灾害发生及生态型的演变特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [2] | 童琪, 王春燕, 阙亚伟, 肖宇, 王政逸. 稻瘟病菌热激蛋白(HSP)40编码基因MoMHF6的鉴定及功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 563-576. |
| [3] | 刘树芳, 董丽英, 李迅东, 周伍民, 杨勤忠. 持有Pi9基因的水稻单基因系IRBL9-W对稻瘟病菌苗期和成株期抗性差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 303-310. |
| [4] | 董俊杰, 曾宇翔, 季芝娟, 梁燕, 杨长登. 273份水稻种质资源的遗传多样性、群体结构与连锁不平衡 分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 130-140. |
| [5] | 孟峰, 张亚玲, 靳学慧. 黑龙江省稻瘟病菌无毒基因AVR-Pita及其同源基因的检测与分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 143-149. |
| [6] | 朱名海, 彭丹丹, 舒灿伟, 周而勋. 海南南繁区水稻纹枯病菌的遗传多样性与致病力分化[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 176-185. |
| [7] | 冯向阳, 张震, 柴荣耀, 邱海萍, 王教瑜, 毛雪琴, 王艳丽, 孙国昌. ATP硫酸化酶基因MoMET3在稻瘟病菌生长发育和致病过程中的功能分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(5): 542-550. |
| [8] | 阮宏椿, 石妞妞, 杜宜新, 甘林, 杨秀娟, 代玉立, 陈福如. 水稻抗性基因Pi对福建省稻瘟病菌优势菌群的抗性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 105-110. |
| [9] | 顾卓侃, 李玲, 王教瑜, 柴荣耀, 王艳丽, 张震, 毛雪琴, 邱海萍, 孙国昌. 利用卡氏白和尼罗红染色观察稻瘟病菌有性世代的结构[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(6): 668-672. |
| [10] | 刘鑫, 张恒, 阚虎飞, 周立帅, 黄昊, 宋林林, 翟焕趁, 张君, 鲁国东. 水稻泛素结合酶基因家族的生物信息学与表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 223-231. |
| [11] | 袁筱萍, 王彩红, 邓宏中, 徐群, 冯跃, 余汉勇, 王一平, 魏兴华. 亚洲栽培稻遗传变异分析最少SSR引物数的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(6): 578-586. |
| [12] | 王玲, 左示敏, 张亚芳, 陈宗祥, 潘学彪, 黄世文. 四川省稻瘟病菌群体遗传结构分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 327-334. |
| [13] | 李贺, 韩艺娟, 林艺娟, 刘丽华, 张承康, 张连虎, 王宗华, 鲁国东. 水稻锌指蛋白基因OsZFP1的功能分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(2): 135-140. |
| [14] | 刘承晨, 赵富伟, 吴晓霞, 张昌泉, 朱孔志, 薛达元, 武建勇, 黄绍文, 徐小颖, 金银根, 刘巧泉. 云南哈尼梯田当前栽培水稻遗传多样性及群体结构分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(1): 28-34. |
| [15] | 陈亚平, 施文骁, 王洪凯. 稻瘟病菌大片段DNA转化载体的构建[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(1): 91-96. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||